“Hindustan” Inverter duty motors are wound with special insulation system viz. dual coated class H wires, special vacuum pressure impregnation (VPI).
INTRODUCTION
These motors are fed with Variable Voltage & Variable Frequency (VVVF) from inverter (VFD) supply to achieve speed variation required by the process / application & to gain energy savings related with speeds. Typical VFDs have a very high switching frequencies which results in generating very high dV/dt (up to 1.2kV/µs). Such high pulses impress severe stresses on the windings. If the motors with standard insulation systems are fed from inverters, the repeated pulses of such surge waves reduces the insulation strength & the life of the motor unpredictably. “Hindustan” Inverter duty motors are wound with special insulation system viz. dual coated class H wires, special vacuum pressure impregnation (VPI).
CONSTRUCTION:
Separate cooling:
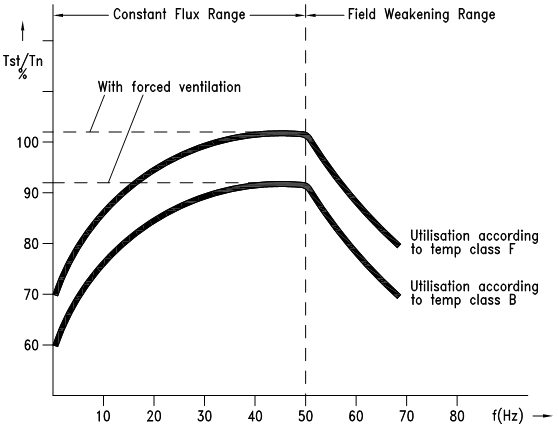
When the motor is run from 5Hz to 50Hz & expected to deliver the rated torque, the motor will draw the rated current. The heating due to the rated current will be equal to the rated heating. At lower speeds, the cooling of the motor is reduced significantly resulting in increased temperature rise. To control this, inverter duty motors are fitted with separate cooling fans. This ensures that the rated cooling is maintained even at reduced speeds.
Insulated Bearing:
It is also suggested to protect motors of frames 315 & above with insulated bearing at non-drive end due to high shaft currents induced, which are detrimental to bearing life. In smaller motors, shaft currents are less, which are taken care of by grease film in the bearing.
Operation at higher speeds:
At frequencies above 50Hz, voltage is maintained constant & only the frequency is increased. This results in reduced V/f ratio resulting in weakened magnetic flux in the motor. Following care should be taken in this operation mode;
- The mechanical speed of the motor should never exceed as below.
Safe Maximum Speed for Motors
|
|---|
Frame Size
| 2P
| 4P
| 6P
| 8P
|
|---|
≤100
| 5200
| 3600
| 2400
| 1800
|
112
| 5200
| 3600
| 2400
| 1800
|
132
| 4500
| 2700
| 2400
| 1800
|
160
| 4500
| 2700
| 2400
| 1800
|
180
| 4500
| 2700
| 2400
| 1800
|
200
| 4500
| 2300
| 1800
| 1500
|
225
| 3600
| 2300
| 1800
| 1500
|
250
| 3600
| 2300
| 1800
| 1500
|
280
| 3600
| 2300
| 1800
| 1500
|
315
| 3600
| 2300
| 1800
| 1500
|
355
| 3600
| 2300
| 1800
| 1500
|
- The output torque reduces greatly with increase in frequency. This results in constant power output.
- The maximum speed & the maximum operating torque possible at any speed should be chosen ensuring the above.